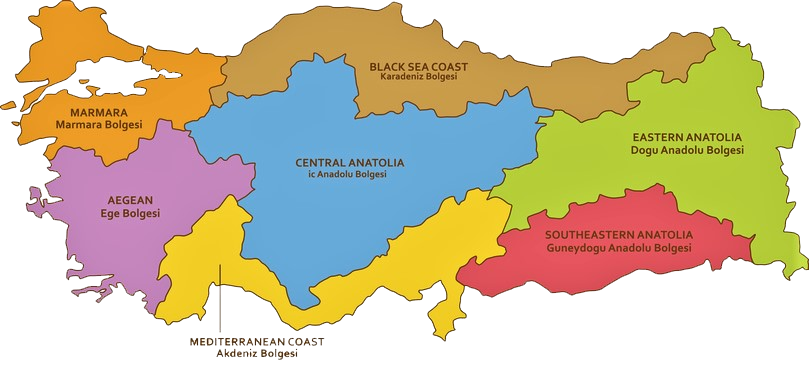
Turkey is more than just beaches. The country is home to a diverse and rich collection of landscapes. Surrounded by three seas, Turkey has some 8000 kilometres of coastline. The country is divided into seven geographical regions: the Aegean, Central Anatolia, Eastern Anatolia, Southeastern Anatolia, Black Sea, Marmara, and the Mediterranean region. The largest land area of Turkey is Anatolia, which connects Turkey to Asia. Most of Anatolia is comprised of narrow coastal plains and high plateaus. In the east, most of the land is mountainous and connected to major river systems.
• Total Area: 783, 562 square km
• Climate: Dry and hot summers and mild winters
• Highest Point: Mount Ararat 5,166 m
• Lowest Point: Mediterranean Sea 0 m